Pāḷi-Thai Tipiṭaka Notation

Tipiṭaka is a repository of the Buddha's word which was the resolution of the First Great Tipiṭaka Council, convened by his disciples immediately after the Buddha attained Nibbāna during the First Buddhist Era (BCE 544-545); thus, the oldest source of the Buddhist Canonical Scriptures. The sound of Tipiṭaka scriptures was transmitted orally for over four centuries in Pāḷi dialect, an ancient language of the Indo-Aryan linguistic family. The Pāḷi Tipiṭaka in oral tradition was inscribed for the first time in Sinhala script on palm-leaves in old Sri Lanka in 110 BCE. Since then, from this cradle of the written scriptures, the Pāḷi text was gradually transliterated into various international scripts of the world and was subsequently translated into different languages.


Roman-Script 2005 Edition, revised in 2019
Despite the translation of the Pāḷi text, the significance of the Pāḷi Tipiṭaka recitation continues to have its functional and sacred legitimacy. It has been continuously practiced as recorded in the Book of Vinayapiṭaka Discipline. Since the Buddha's time, the Pātimokkhapāḷi Disciplinary Rules are to be recited by the monastic community every fortnight in the pristine purity of the original Pāḷi sound. Furthermore, it is of the utmost importance that each sound of the alphabet must be enunciated correctly in accordance with the place and the manner of articulation in the Pāḷi Tipiṭaka grammar. For instance, a monk who mispronounces an aspirated sound to be unaspirated sound or vice versa during the all important oral ordination preception, will thereby commit an offense and the ordination will not be consummated (see Mahāsaṅgīti Tipiṭaka Buddhavasse 2500, Vol. 5, Vinayapiṭaka, Parivāravagga No. 455, and No. 485 in Roman-Script 2005 Edition).


The world's first printed set of the Pāḷi Tipiṭaka was the 39-volume Chulachomklao of Syām 1893 Edition, then written in Syām-script, a new orthographic writing system. The Syām-script orthography was uniquely invented with distinctive Pāḷi phonetic symbols to differentiate between non-final consonant, final-consonant and cluster-consonant syllables. These three phonetic symbols in Syām-script were regarded not only as the most complete printed Tipiṭaka transliteration in book form but also the pioneering phonetic transcription of the day.

Royal Gift for St. Andrews University in 1895
It was commissioned by King Chulalongkorn Chulachomklao of Syām (present-day Thailand) who later presented this magnum opus as royal gifts of Dhamma to over 260 institutions worldwide, including, Carolina Rediviva at Uppsala University in Sweden, Komazawa University in Japan, St. Andrews University in Scotland, UK; Temple of the Holy Tooth Relic, Kandy, Ceylon (present-day Sri Lanka), Imperial Academy of Arts and Sciences in St. Petersburg, present-day Russian Federation; Hong Kong, present-day Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China; and College of New Jersey, now present-day Princeton University, USA.

The Roman-script transliteration for printing the Pāḷi text was introduced in Europe in 1888. However the complete Roman-script Pāḷi Tipiṭaka Edition in forty volumes, based on the latest International Tipiṭaka Council 1957 Edition, was published in 2005 in Bangkok by the World Tipiṭaka Project. The new proofreading and Roman-script typesetting, as well as the creation of the first phase of the Tipiṭaka database in XML format was undertaken under the patronage of His Holiness Prince Krom Luang Vajirañanasaṁvara, the Supreme Patriarch of Thailand, who himself was one of the representative Pāḷi scholars from Thailand to attend the historic international council in Yangon, the old capital of Myanmar (formerly Burma). The new edition was entitled Mahāsaṅgīti Tipiṭaka Buddhavasse 2500 (The Great International Tipiṭaka Council B.E. 2500/1957 Edition). The special inaugural edition was presented to President Chandrika Bandaranaike Kumaratunga of Sri Lanka as a royal gift of Dhamma from Her Royal Highness Princess Galyani Vadhana, grand-daughter of King Chulalongkorn Chulachomklao. The Princess Patron made a special Tipiṭaka Pilgrimage to Colombo upon an invitation of the President of Sri Lanka.
Today over 150 special sets have been presented to the leading international libraries worldwide. Recently, the second edition in Roman-script published in 2019 with the newly revised International Phonetic Alphabet in Pāḷi (Pāḷi IPA), was presented to the British Library in London for the special exhibition on Buddhism, between 2019-2020.

The World Tipiṭaka Innovation 1999-present
In 2014, Professor Dr. Chidchanok Lursinsup, a Royal Fellow in the Science Academy of Thailand, published a groundbreaking article, employing sixty-one mathematical formulae to decode the Syām-script orthographic writing of Chulachomkloa Edition. His references were based on Kaccāyana Vyākaraṇapāḷi, the oldest and one of the most important exegesis of the Pāḷi Grammar, as well as Pāḷi-Syām to Pāḷi-Roman phonetic transcriptions. The analysis confirmed that Syām-script edition, was in fact a linguistic innovation in phonetic transcription and syllabic segmentation for the Pāḷi Tipiṭaka publication a century ago. The "Chidchanok Mathematical Formulae", made it possible for the World Tipiṭaka Project to develop an automatic computer program for syllabic segmentation of the entire World Tipiṭaka Edition in forty-volumes.


Chidchanok Mathematical Formulae 2014
In 2014, the World Tipiṭaka Foundation received a Patent No. 46390, entitled the syllabic segmentation programme for the electronic devices in accordance with the 1893 Syām-script orthography. Hence the new possibility for the World Tipiṭaka Project to study linguistically the electronic database corpus of the digital Tipiṭaka, comprising 2,767,074 words, 9,422,422 syllables, or 20,946,860 characters in Roman scripts.

Digital Sajjhāya Recitation Sound 2017
The Pāḷi Tipiṭaka Notation is the final phase of the World Tipiṭaka Project (1999-present). It aims to integrate the traditional Pāḷi transliteration of monastic culture into the Pāḷi phonetic transcription in modern linguistics, as well as to create a new notation in musical symbol as an international standard. Based on the World Tipiṭaka Patent No. 46390 and pronunciation rules of the Pāḷi Tipiṭaka Grammar of old, Dr. Sasi Pongsarayuth, Associate Professor of music from Chulalongkorn University, proposed an international musical notation for the new Pāḷi Tipiṭaka transcription, in order to replicate the recitation sound of the Tipiṭaka scriptures. To transcribe the Pāḷi sound into the new notation, 95 different symbols have to be created.
There are four versions of the Pāḷi Tipiṭaka Notation for four different study purposes, namely:
1. Lahu (one metre) and Garu (two metres) rhythms

4. Digital electronics
 Each version comprising of 250 volumes is now available both in book form and digital data file.
Each version comprising of 250 volumes is now available both in book form and digital data file.
The digital audio recording from the Pāḷi Tipiṭaka Notation Edition amounts to 3,052 hours or 1.6 Terabytes.

Pāḷi Phonetic Transcription 2014







In 2017, the recording of the Pāḷi Tipiṭaka Notation or the Digital Sajjhāya Recitation Sound was successfully synthesized into electronic devices as manufacturing prototypes for smart phone and tablet models. An example of a Sajjhāya electronic device was selected for Digital Big Bang Exhibition in Bangkok 2019.

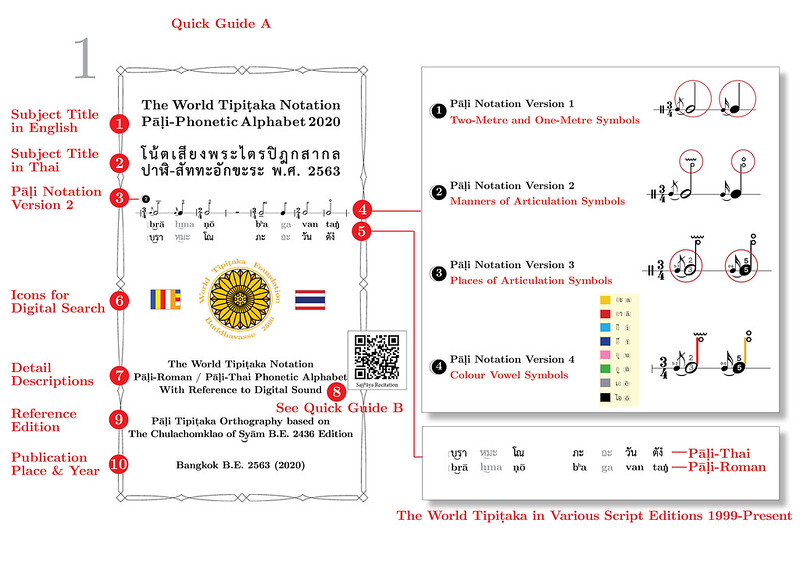



Today, the Pāḷi Tipiṭaka Notation is typeset electronically in a new parallel corpus for the digital database, which can be published with four different sets of the phonetic alphabet combinations for study and easy pronunciation.The Pāḷi Notation Project was selected by National Research Council of Thailand to exhibit at the 48th International Exhibition of Inventions Geneva and finally received a medal and certificate for one of the best research innovations.
worldwide; namely:
1. Pāḷi-Roman Script Notation
(English speaking community)


2. Pāḷi-Tai Script Notation
(Tai and Thai community),


3. Pāḷi-Kirillitsa Script Notation
(Cyrillic culture in Russia & E. Europe),


4. Pāḷi-Pinyin Notation
(Chinese speaking community)


The new Pāḷi Tipiṭaka Notation is therefore an innovation in the interdisciplinary studies of the digital Pāḷi text, cultural linguistics and applied musicology. The recitation of the Pāḷi sound can be strictly transcribed with digital accuracy both linguistically and electronically into international musical symbols and notational scores for the first time. It is the culmination of the international efforts to replicate the sound of the Buddha's word, or The Pāḷi Code; comprising of forty-one Pāḷi consonants and eight pure vowel sounds, which was committed to memory by his erudite and enlightened disciples, as recorded in the First Great Tipiṭaka Council over two millennia ago.



British Library Exibition in London 2019-2020
This complete digital transformation of the Pāḷi Tipiṭaka into the World Tipiṭaka Big Data is aimed to facilitate further development of the Tipiṭaka Artificial Intelligence Technology. With the recent breakthrough of the World Tipiṭaka digital transformation, it is now possible for the World Tipiṭaka Foundation to make this digital wisdom-base available not only for international students of the Tipiṭaka studies in various cultural traditions, but also the scholars of interdisciplinary studies, particularly in digital-based knowledges, in areas which are not traditionally associated with the Pāḷi text, such as musicology, acoustical engineering and medical science technology, but whose potential expertise can contribute immensely to the future society and the sustainable well-being of humanity, both body and mind.
Digital Sajjhāya Recitation Sound
Postscript 2024
Her Royal Highness Princess Galyani Vadhana of Thailand, the beloved Aunt and the Royal Matriarch of the King and Founding Honourary President of the World Tipiṭaka Project, was declared by UNESCO the 2023 Eminent Personality of the World. Her scholarly dissemination worldwide of the world's first complete, 40-volume Roman-Script Transliteration of the Tipiṭaka 2005 Edition was one of her most remarkable contributions to the world. The Government of Thailand had organized a year-long centenary celebration for the late Princess which culminated in the Buddhist Merit-Making Ceremony in the Grand Palace, presided by Their Majesties the King and Queen.
It is fitting that in 2023 Thailand Research Council selected the World Tipiṭaka's Pāḷi Monotone Music Notation and it's Saj-jʰā-ya Electronic Devices to exhibit at the 48th International Exhibition of Inventions in Geneva, Switzerland. This meritorious project, a fruit of the Princess's vision, was honoured with a Medal and a Certificate from the international community.
In 2024 the Ministry of Foreign Affairs included the Dissemination of the Saj-jʰā-ya Phonetic Recitation Tipiṭaka Project to be part of the Government of Thailand's celebration of the auspicious 72nd Birthday Anniversary of His Majesty the King, Rama X, in 28 July 2024. In 2016 His Majesty The King graciously presided over the Chairmanship of this Commemorative Publication in homage of the Dhamma as well as to honour H.M. King Bhumibol Adulyadej, Rama IX, the King Father and H.M. Queen Sirikit the Queen Mother.
Over a century ago by the royal command of King Chulalonkorn Chulachomklao, Rama V, the Foreign Ministry, Kingdom of Syām, organized the logistics of distributing the Tipiṭaka to over 25 countries in five continents. Today, no less than 36 sets of this special 80-volume commemorative publication will be presented as a Gift of Peace and Wisdom from Bangkok to the Royal Thai Embassies around the world. The Thai ambassadors will consequently bequest these special gifts to leading international libraries worldwide, thereby following the historic Royal Gift of the Syām-Script Pāḷi Tipiṭaka 1893 Edition from King Chulalongkorn Chulachomklao of Syām.
A note on the digital Saj-jʰā-ya Recitation Audio :
The chief Saj-jʰā-ya Reciter, was Brig. Gen. Suradhaj Bunnag, who was the founder of the World Tipiṭaka Project and editor of the Saj-jʰā-ya Phonetic Edition since 2009. Bunnag had a training in Western voicing as well as in Pāḷi Grammar pronunciation in the Theravāda monastic tradition. His pilot recording during 2009-2010 was made under the supervision of Thailand's eminent Tipiṭaka Master Siri Petchai and Professor Kancana Ngawrangsri, (Ph.D., Linguistics, University of Copenhagen). The pilot recitation was based on the new set of the Pāḷi Phonetic Alphabet proposed at the Royal Academy in 2013 by Professor Vichin Phanupong (Ph.D., SOAS, Linguistics), Department of Linguistics, Faculty of Arts, Chulalongkorn University.
The final and complete recording was made in 2016. It was the first digital audio sound recording to have Lahu-Garu rhythmic articulation since it was clearly recited from the newly-proposed monotone music notation by Associate Professor Dr. Sasi Pongsarayuth, Head of the Western Music Department, Faculty of Applied Arts, Chulalongkorn University. The digital recording production was directed under the supervision of Professor in Voicing, Duanjai Tewtong, Faculty of Applied Arts, Chulalongkorn University.
Pali-thai / Pali-Roman Nota... by Dhamma Society on Scribd


